Diabetes is a chronic condition that can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes. Regular eye examinations are crucial for individuals with diabetes to detect and manage potential eye-related complications early.
Why Are Regular Eye Exams Essential for Diabetic Patients?
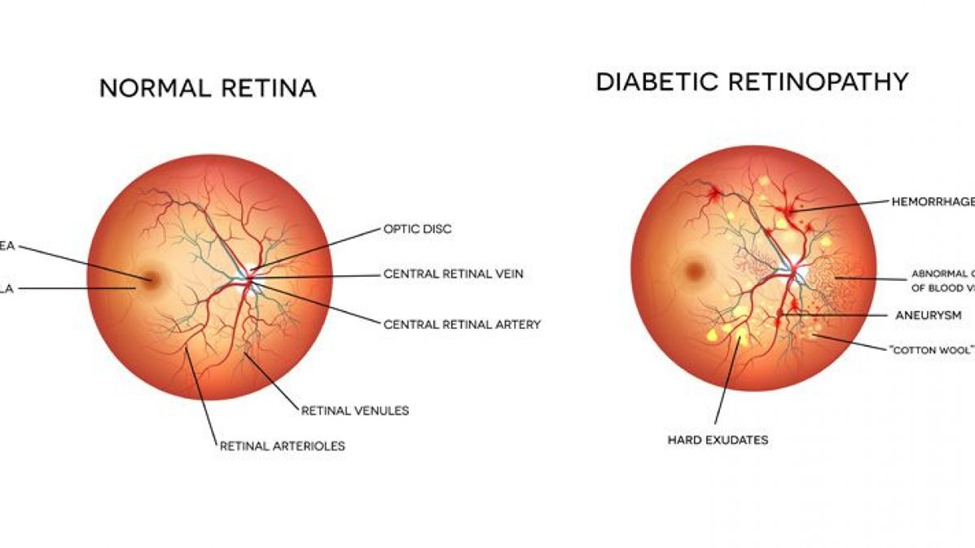
1.Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina. Early stages may not present noticeable symptoms, making regular eye exams vital for early detection and treatment.
2.Monitoring for Other Eye Conditions: Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk for other eye conditions, including cataracts and glaucoma. Regular eye exams can help in early identification and management of these conditions.
3.Preventing Vision Loss: Early detection and treatment of diabetic eye diseases can prevent significant vision loss or blindness. Regular eye exams allow for timely intervention, preserving eye health and vision.
Recommended Frequency of Eye Exams
•Type 1 Diabetes: An initial comprehensive eye examination should be conducted within five years of diagnosis, followed by annual exams.
•Type 2 Diabetes: An eye examination should be performed at the time of diagnosis, with subsequent annual exams.
•Pregnancy: Women with diabetes who are planning pregnancy should have an eye exam before conception and during the first trimester, with close follow-up throughout pregnancy.
What to Expect During an Eye Exam
A comprehensive eye exam for a diabetic patient typically includes:
•Visual Acuity Test: Assesses the clarity of vision.
•Dilated Eye Exam: Drops are used to widen the pupils, allowing the eye care professional to examine the retina and optic nerve for signs of damage.
•Tonometry: Measures the pressure inside the eye to check for glaucoma.
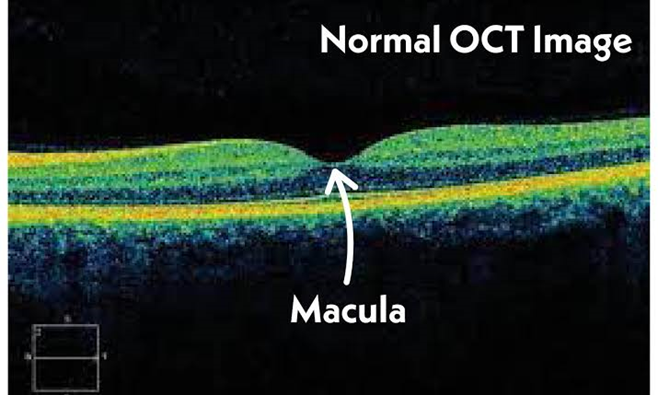
•Macula OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography): Macular Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the macula, enabling detailed assessment of its structure and aiding in the diagnosis and management of various retinal conditions like diabetic retinopathy.
Maintaining Eye Health
In addition to regular eye exams, diabetic patients should:
•Manage Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood glucose levels within the target range can slow the onset and progression of diabetic retinopathy.
•Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: High blood pressure and cholesterol can exacerbate eye problems; maintaining them within recommended levels is beneficial.
•Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking contribute to overall health and can reduce the risk of diabetic complications.
Conclusion
Regular eye examinations are a critical component of diabetes management. They enable early detection and treatment of eye-related complications, significantly reducing the risk of vision loss. Patients with diabetes should adhere to the recommended schedule for eye exams and maintain good control of their blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels to preserve their eye health.